Pneumonia is a serious respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding pneumonia symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This article dives deep into the symptoms, causes, types, treatment options, and preventive measures to help you stay informed about this condition.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs (alveoli) in one or both lungs. These air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, causing breathing difficulties and other symptoms. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or even chemical irritants.
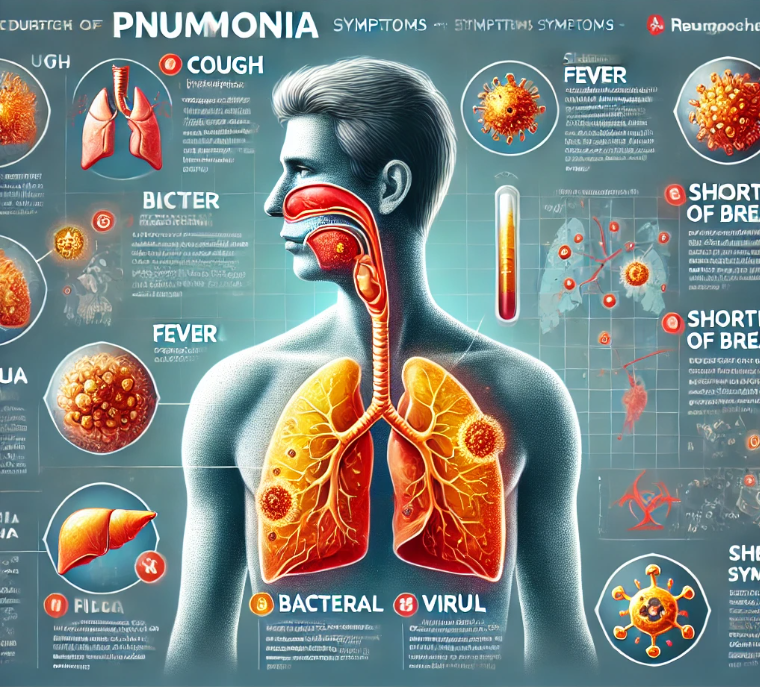
Common Pneumonia Symptoms
Recognizing pneumonia symptoms early can significantly improve outcomes. Below are the most common symptoms:
| Pneumonia Symptoms | Details |
|---|---|
| Cough | Persistent, often producing mucus or phlegm, which may be yellow, green, or blood-tinged. |
| Fever | High fever accompanied by chills or shaking. |
| Shortness of Breath | Difficulty in breathing or feeling breathless. |
| Chest Pain | Sharp or stabbing pain that worsens when breathing deeply or coughing. |
| Fatigue | Extreme tiredness and weakness. |
| Nausea or Vomiting | Common in children and older adults. |
| Confusion | Especially seen in older adults or those with severe infections. |
What Causes Pneumonia?
Understanding what causes pneumonia is essential for prevention. The primary causes are:
- Bacterial Pneumonia: Often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. This type can occur independently or as a complication of the flu.
- Viral Pneumonia: Commonly caused by respiratory viruses, including the flu and COVID-19.
- Fungal Pneumonia: Caused by fungi such as Histoplasma or Pneumocystis jirovecii, more common in immunocompromised individuals.
- Aspiration Pneumonia: Occurs when food, drink, vomit, or saliva is inhaled into the lungs.
Types of Pneumonia
There are several types of pneumonia, each with unique characteristics:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Community-Acquired | Contracted outside hospitals, often bacterial or viral. |
| Hospital-Acquired | Contracted during a hospital stay, usually more severe and antibiotic-resistant. |
| Aspiration Pneumonia | Caused by inhaling foreign material into the lungs. |
| Walking Pneumonia | A milder form caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, often mistaken for a common cold. |
| Lobar Pneumonia | Affects a specific section (lobe) of the lung. |
| Bronchopneumonia | Spreads throughout the lungs, affecting patches of lung tissue. |
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
One of the most common questions is: Is pneumonia contagious? The answer depends on the cause:
- Bacterial Pneumonia: Can be contagious through respiratory droplets.
- Viral Pneumonia: Highly contagious, especially during flu season.
- Fungal Pneumonia: Generally not contagious, as it is caused by environmental fungi.
Is Pneumonia Deadly?
Is pneumonia deadly? The answer varies based on age, overall health, and access to medical care. While most healthy individuals recover with timely treatment, it can be life-threatening for:
- Infants and young children.
- Older adults (65+ years).
- Individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic conditions.
Globally, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death in children under five, emphasizing the importance of early detection and prevention.
Pneumonia Treatment Options
Pneumonia treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection:
- Antibiotics: Used for bacterial pneumonia.
- Antiviral Medications: Effective against viral pneumonia.
- Antifungal Medications: Prescribed for fungal pneumonia.
- Oxygen Therapy: Helps with breathing difficulties in severe cases.
- Hospitalization: Required for severe infections, especially for those with complications like sepsis or respiratory failure.
Most cases of pneumonia can be managed effectively if treated promptly. This raises the question: Is pneumonia curable? The answer is a resounding yes for most cases, although recovery may take weeks or even months.
Prevention of Pneumonia
Prevention of pneumonia is key to reducing its impact. Here are effective measures:
- Vaccination: Get vaccinated against pneumococcal pneumonia, the flu, and COVID-19.
- Hygiene Practices: Wash hands frequently and use sanitizers to prevent the spread of germs.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking to keep your lungs healthy.
- Avoid Exposure: Stay away from individuals showing symptoms of respiratory infections.
FAQs about Pneumonia Symptoms and Treatment
1. What are the early signs of pneumonia?
The early signs include fever, cough, chills, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
2. What causes pneumonia in children?
In children, pneumonia is often caused by viruses like the flu or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
3. Is pneumonia contagious during treatment?
Yes, bacterial and viral pneumonia can remain contagious during the initial phase of treatment.
4. Is pneumonia deadly if left untreated?
Yes, untreated pneumonia can lead to severe complications, including respiratory failure and sepsis.
5. What is the fastest way to recover from pneumonia?
Follow the prescribed pneumonia treatment, rest adequately, stay hydrated, and eat nutritious food to aid recovery.
6. Is pneumonia curable without antibiotics?
No, bacterial pneumonia requires antibiotics. Viral pneumonia may resolve on its own, but antiviral drugs can help in some cases.
7. How do I prevent pneumonia in older adults?
Vaccinations, a healthy lifestyle, and prompt treatment of respiratory infections are vital for prevention in seniors.
8. What are the types of pneumonia vaccines available?
Two primary vaccines are the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23).