Good posture is more than just standing tall or sitting straight; it is about maintaining the natural alignment of your body, ensuring balance, and preventing unnecessary strain on muscles and ligaments. With our increasingly sedentary lifestyles and the prevalence of technology, poor posture has become a common issue. Let’s explore why posture is crucial and how to adopt and maintain it for optimal health.
What Is Good Posture?
Good posture refers to the correct alignment of your body while sitting, standing, or moving. This alignment minimizes stress on muscles, joints, and ligaments, allowing your body to function efficiently.
5 Types of Posture:
| Posture Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Neutral Posture | Balanced alignment, with minimal strain on the body. |
| Kyphosis | Excessive forward rounding of the upper back. |
| Lordosis | Exaggerated inward curve of the lower back. |
| Flat Back | Loss of natural spinal curve, leading to stiffness. |
| Swayback | Hips pushed forward, causing an uneven alignment. |
The Importance of Good Posture
Proper posture plays a pivotal role in physical health and mental well-being. Here are the 8 benefits of good posture:
- Reduces Back and Neck Pain: Good posture decreases strain on your spine and prevents chronic pain.
- Boosts Energy Levels: When your body is aligned, you expend less energy, leaving you feeling less fatigued.
- Improves Breathing: An upright posture allows better lung expansion, enhancing oxygen flow.
- Enhances Digestion: Sitting or standing correctly reduces compression on abdominal organs, aiding digestion.
- Promotes Better Circulation: Proper posture prevents restricted blood flow, reducing the risk of varicose veins.
- Strengthens Core Muscles: Maintaining posture engages and strengthens your core.
- Increases Confidence: A good posture projects self-assurance and can positively impact mental health.
- Improves Athletic Performance: Balanced alignment optimizes muscle function and movement efficiency.
For more insights, you can refer to the “importance of good posture pdf” documents often found online for detailed scientific studies.
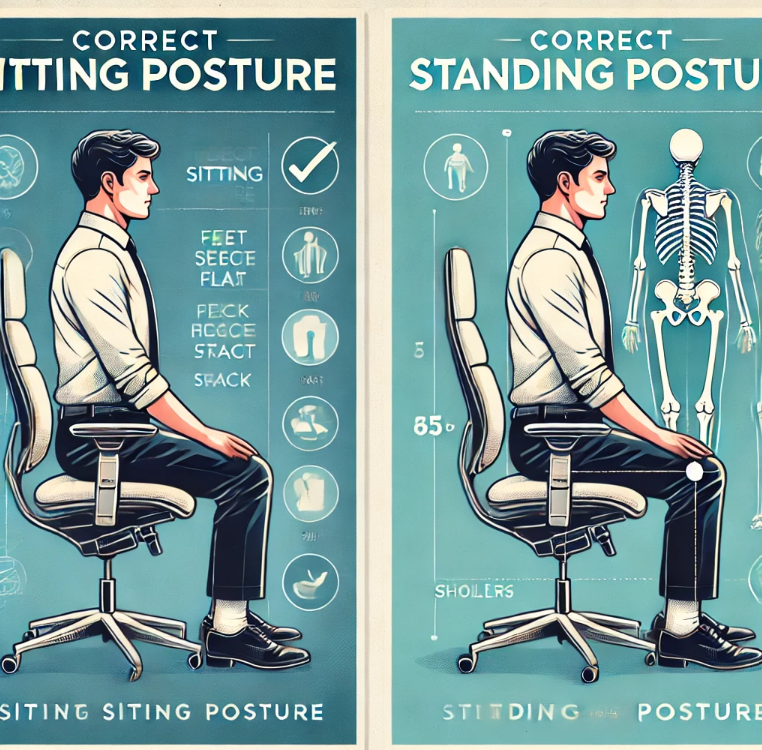
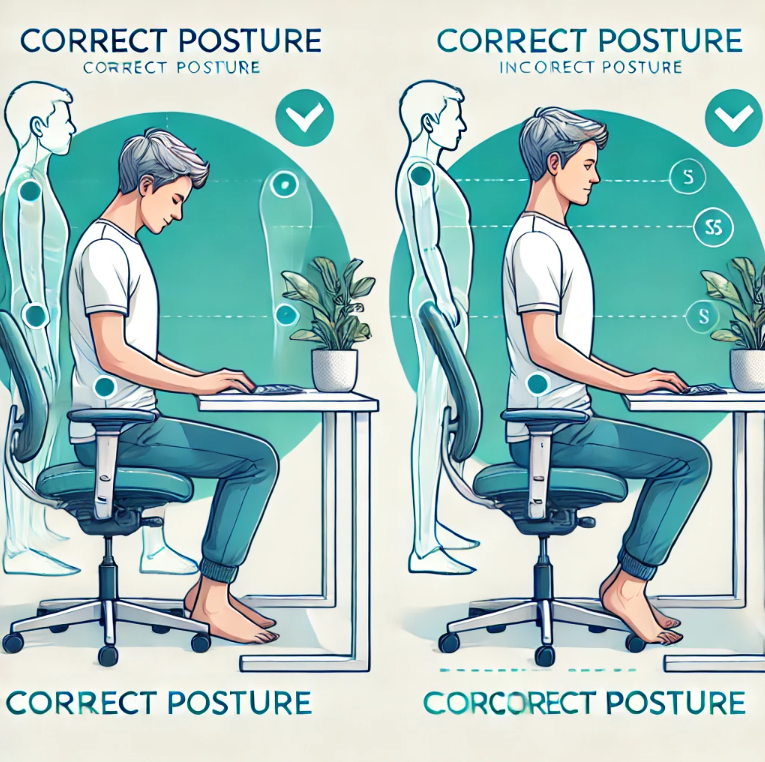
Tips for Good Posture While Sitting
Maintaining good posture while sitting is essential, especially for individuals who spend long hours at desks. Here’s how to have good posture when sitting:
- Use an Ergonomic Chair: Ensure your chair provides lumbar support and keeps your back straight.
- Keep Feet Flat on the Floor: Avoid crossing your legs; your feet should be flat with knees at a 90-degree angle.
- Position Your Screen Correctly: Keep your monitor at eye level to avoid straining your neck.
- Sit Back Fully: Your back should rest against the chair for support.
- Engage Your Core: Slightly tighten your abdominal muscles to support your lower back.
- Take Frequent Breaks: Stand up and stretch every 30-60 minutes to relieve pressure.
| Correct Sitting Posture Checklist | Common Mistakes |
| Feet flat on the ground | Crossing legs |
| Back fully supported | Leaning forward |
| Shoulders relaxed | Hunching shoulders |
| Screen at eye level | Tilting head downward |
Tips for Good Posture While Standing
Standing properly distributes your body weight evenly and reduces strain. Here’s how to achieve a correct standing posture:
- Align Your Ears, Shoulders, and Hips: Imagine a straight line running through these points.
- Keep Your Knees Slightly Bent: Avoid locking your knees to prevent joint strain.
- Distribute Weight Evenly: Balance your weight between both feet.
- Engage Your Core Muscles: Maintain a slight contraction to support your lower back.
- Relax Your Shoulders: Keep them down and slightly back to avoid slouching.
How to Permanently Fix Posture
Correcting posture requires consistency and awareness. Follow these steps for long-term improvements:
- Practice Regular Exercises: Strengthen core and back muscles with activities like yoga, pilates, or resistance training.
- Stretch Daily: Focus on flexibility exercises to release tight muscles, especially in the chest and shoulders.
- Use Posture-Correcting Tools: Devices like posture braces or ergonomic furniture can provide immediate support.
- Be Mindful: Regularly check your posture throughout the day and make adjustments as needed.
- Consult a Professional: Seek advice from physiotherapists or chiropractors for personalized solutions.
Examples of Good Posture
Here are some good posture examples for different activities:
- Sitting: Feet flat, back supported, shoulders relaxed.
- Standing: Weight distributed evenly, spine neutral, shoulders back.
- Walking: Chin parallel to the ground, arms swinging naturally by your sides.
- Sleeping: Use a supportive pillow to align your head with your spine.
Comparing Good and Poor Posture
| Aspect | Good Posture | Poor Posture |
| Spinal Alignment | Natural curves maintained | Excessive rounding or arching |
| Muscle Strain | Minimal strain | Increased strain on specific muscle groups |
| Energy Levels | Higher energy due to efficient movement | Fatigue due to inefficient body mechanics |
FAQs on Posture
- How to have good posture when sitting? Ensure your back is fully supported, feet flat, and monitor at eye level.
- What are some good posture examples? Standing tall with shoulders back, sitting with feet flat, and lying down with proper support.
- What are the 8 benefits of good posture? Improved breathing, reduced pain, better circulation, enhanced digestion, increased energy, stronger core, greater confidence, and better athletic performance.
- How to permanently fix posture? Incorporate regular exercise, stretching, ergonomic tools, and mindfulness into your routine.
- What is a correct standing posture? Stand with ears, shoulders, and hips aligned, knees slightly bent, and shoulders relaxed.
- Why is the importance of good posture pdf significant? These resources offer in-depth research and guidelines for understanding and improving posture.
- What are the 10 benefits of good posture? Along with the 8 listed earlier, add reduced risk of injury and improved mental health.
- What are the 5 types of posture? Neutral posture, kyphosis, lordosis, flat back, and swayback.


