The gut microbiome, a bustling community of trillions of microorganisms residing in our digestive tract, has emerged as a significant player in not just physical health but also mental well-being. This intricate relationship between the gut and brain, often referred to as the gut-brain axis, has been the subject of numerous studies and discussions. The findings suggest that the balance of bacteria in the gut can influence our mood, cognitive functions, and even behaviors. This article delves into the fascinating connection between the gut microbiome and mental health, supported by the latest research, practical tips, and common queries answered.
Understanding the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome comprises bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms that live in the digestive tract. A healthy gut microbiome is diverse and balanced, with beneficial bacteria playing critical roles in digestion, immune function, and neurotransmitter production.
What is one type of bacteria found in a healthy gut microbiome?
Bifidobacteria is one such type of beneficial bacteria commonly found in a healthy gut. It aids in breaking down dietary fiber, producing essential vitamins, and maintaining a strong gut lining.
On the other hand, an imbalance—where harmful bacteria outnumber beneficial ones—can lead to various health issues. But what do harmful bacteria do in the gut microbiome? They can disrupt digestion, weaken immunity, and contribute to inflammation, which may negatively impact mental health.
The Gut-Brain Axis: How the Gut Influences the Mind
The gut and brain communicate through a bidirectional pathway involving:
- Vagus Nerve: Acts as a direct communication line.
- Neurotransmitters: Gut bacteria produce chemicals like serotonin, a key player in mood regulation.
- Immune System: Gut health influences inflammation, which can affect the brain.
Latest Research on Gut Microbiome and Mental Health
Recent gut microbiome research papers highlight the connection between gut bacteria and mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. For instance, a 2024 study published in the Journal of Microbiome Health showed that individuals with depression had significantly lower levels of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
Another notable finding from a gut microbiome book by Dr. Emeran Mayer emphasizes that improving gut health can alleviate symptoms of stress and anxiety.
| Factor | Healthy Gut Microbiome | Imbalanced Gut Microbiome |
|---|---|---|
| Microbial Diversity | High | Low |
| Mental Health Impact | Positive | Negative |
| Inflammation Levels | Low | High |
| Key Neurotransmitter Production | Optimal | Impaired |
How to Improve Gut Microbiome for Better Mental Health
Maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is crucial. Here are some actionable tips:
- Dietary Changes
- Eat Fermented Foods: Include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
- Consume Prebiotics: Foods like garlic, bananas, and onions feed good bacteria.
- Limit Processed Foods: These can promote harmful bacterial growth.
- Exercise Regularly
- Physical activity enhances microbial diversity.
- Manage Stress
- Stress negatively affects the gut. Practices like meditation and deep breathing can help.
- Consider a Gut Microbiome Test
- These tests analyze your gut bacteria composition, providing insights into how to improve gut microbiome.
- Stay Updated on Research
- Refer to the latest research on gut microbiome for evidence-based approaches.
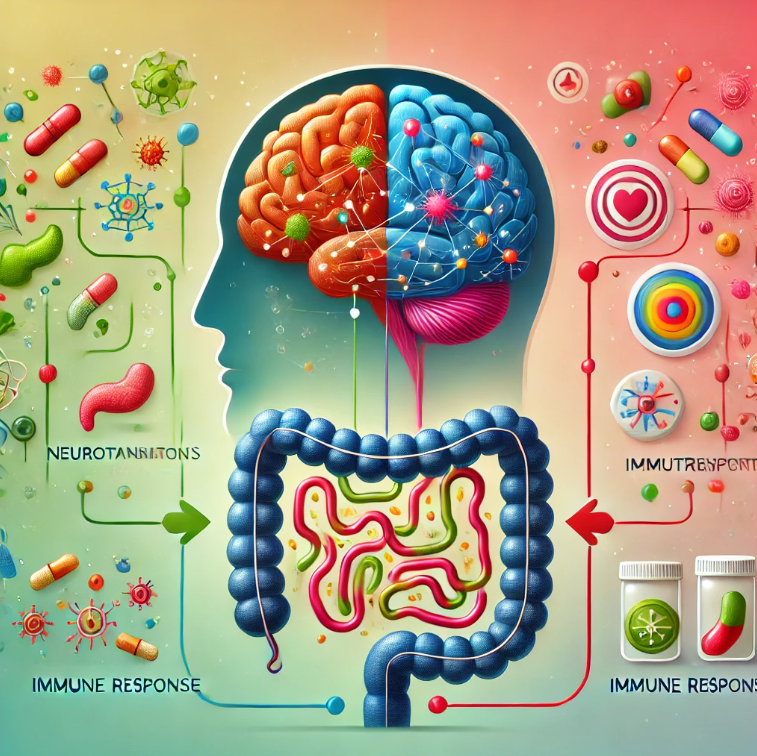
Gut Microbiome and Health: Beyond the Brain
While mental health is a significant aspect, the gut microbiome’s impact extends to:
- Immune System Regulation: A robust microbiome supports immunity.
- Metabolic Health: It aids in weight management and energy production.
- Chronic Diseases: Research links gut health to conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
FAQs on Gut Microbiome and Mental Health
Q1: What is one type of bacteria found in a healthy gut microbiome? A1: Bifidobacteria, which help in digestion and immunity.
Q2: What do harmful bacteria do in the gut microbiome? A2: They disrupt digestion, increase inflammation, and negatively affect mental health.
Q3: How to improve gut microbiome for mental health? A3: Adopt a diet rich in prebiotics and fermented foods, exercise, manage stress, and consider a gut microbiome test.
Q4: What are gut microbiome tests? A4: These are diagnostic tools that assess the types and levels of bacteria in your gut, guiding personalized health interventions.
Q5: Where can I find the latest research on gut microbiome? A5: Look for gut microbiome research papers in journals like Microbiome and Nature Medicine.
Q6: Can a gut microbiome book help in understanding this topic? A6: Absolutely! Books like The Mind-Gut Connection by Emeran Mayer provide valuable insights.
Q7: What is the connection between gut microbiome and health overall? A7: The gut microbiome influences digestion, immunity, metabolism, and mental health.
Q8: Are there specific diets recommended for gut health? A8: Yes, plant-based and fiber-rich diets are often recommended for a healthier microbiome.
In conclusion, the connection between the gut microbiome and mental health underscores the importance of a balanced and diverse gut ecosystem. By understanding the science and implementing simple lifestyle changes, we can enhance not only our mental well-being but overall health. Stay informed with the latest research and prioritize gut health to reap its multifaceted benefits.