Salt is an essential nutrient for the human body, playing a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions. However, consuming too much salt in one day can lead to a range of negative effects on your health. While moderate salt intake is necessary, excess salt consumption can pose significant risks. This blog delves into the symptoms of overconsumption, its side effects, and actionable steps you can take to mitigate these effects.
Why Salt Matters
Salt, or sodium chloride, is indispensable for maintaining the body’s water balance. The recommended daily intake of sodium is around 2,300 milligrams for adults, which is equivalent to about one teaspoon of table salt. Consuming more than this amount regularly or in a single day can result in adverse health effects.
Symptoms of Eating Too Much Salt in One Day
1. Swelling (Edema)
Excess salt causes your body to retain water, leading to noticeable swelling, particularly in the hands, feet, and face. This condition, known as edema, is one of the first signs of consuming too much salt.
2. Increased Thirst
When you eat salty foods, your body craves water to balance the sodium levels. This excessive thirst can make you feel dehydrated, even if you’ve had plenty of fluids.
3. Headaches
Too much sodium can lead to dehydration and an increase in blood pressure, both of which may cause headaches. The effects of salt on the body can be particularly noticeable in people sensitive to sodium.
4. High Blood Pressure
Salt increases the volume of blood by retaining water, which can spike your blood pressure temporarily or even lead to chronic hypertension if high salt intake persists.
| Salt Intake | Potential Blood Pressure Impact |
|---|---|
| Within limits | Maintains normal blood pressure |
| High intake | Temporary or sustained increase |
5. Stomach Issues
Overeating salt can irritate the stomach lining, potentially causing discomfort or increasing the risk of gastric issues in the long term.
6. Dizziness
Too much salt symptoms dizziness can occur due to an imbalance in electrolytes and dehydration, making you feel lightheaded or unsteady.
7. Frequent Urination
Excess sodium makes your kidneys work harder to expel the surplus through urine, which can lead to more frequent trips to the bathroom.
8. Fatigue and Weakness
A high sodium level can disrupt the balance of potassium and other vital minerals, leading to feelings of tiredness and muscle weakness.
What Happens If You Eat Too Much Salt in One Sitting?
Consuming a large quantity of salt in one sitting can result in immediate effects such as:
- Dehydration: Your body uses extra water to process the salt, leading to dry mouth and thirst.
- Stomach Cramps: Sodium overload can upset your digestive system, causing pain or bloating.
- Rapid Blood Pressure Spike: This may increase the risk of cardiovascular events in people with pre-existing conditions.
I Ate Too Much Salt, What Should I Do?
If you realize you’ve consumed too much salt, take these steps to counteract its effects:
- Drink Water: Hydration helps flush out excess sodium from your system.
- Eat Potassium-Rich Foods: Foods like bananas, spinach, and avocados can help balance sodium levels.
- Exercise: Light physical activity can help regulate your blood pressure.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Stick to fresh, whole foods to avoid adding more salt to your diet.
- Monitor Symptoms: Watch for any signs like dizziness, headaches, or swelling.
| Remedies After Overeating Salt | Benefits |
| Drink plenty of water | Dilutes sodium concentration |
| Eat potassium-rich foods | Balances electrolytes |
| Avoid salty foods | Prevents further sodium intake |
How Much Salt Is Too Much in a Day?
While the recommended daily limit is 2,300 milligrams, most people consume closer to 3,400 milligrams daily, often from processed foods. Surpassing 5,000 milligrams in a day is considered excessive and can trigger noticeable symptoms.
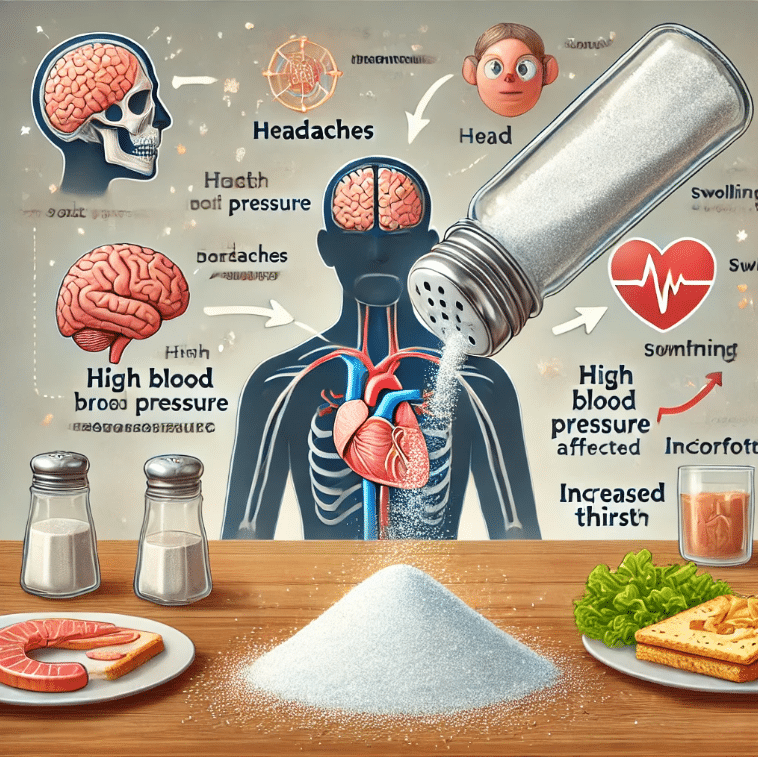
Effects of Salt on the Body
Chronic overconsumption of salt can lead to long-term health issues such as:
- Hypertension: Persistent high blood pressure increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Kidney Damage: Excess sodium puts extra strain on the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney disease.
- Bone Weakness: High salt intake can cause calcium to leach from the bones, increasing the risk of osteoporosis.
Ate Too Much Salt Before Bed?
Eating salty foods late at night can disrupt your sleep by causing:
- Frequent Urination: Increased sodium levels make your kidneys work overtime.
- Restlessness: High sodium intake can elevate blood pressure, making it harder to relax.
- Swelling: Overnight water retention can lead to puffy eyes and face in the morning.
FAQs About Eating Too Much Salt
1. What are the immediate side effects of eating too much salt?
Immediate effects include thirst, swelling, headaches, and elevated blood pressure.
2. How can I quickly reduce salt in my body?
Drinking water, eating potassium-rich foods, and exercising can help flush out excess sodium.
3. Can too much salt cause dizziness?
Yes, electrolyte imbalance and dehydration from excess salt can cause dizziness.
4. What happens if you eat too much salt in one sitting?
You may experience stomach discomfort, headaches, and a temporary spike in blood pressure.
5. Is drinking water enough to counteract salt?
While water helps, combining hydration with a potassium-rich diet is more effective.


