Fats are an essential component of the human body, serving as a source of energy and playing critical roles in various physiological processes. While the term “fat” is often associated with negative health implications, the reality is more nuanced. Understanding the different types of fats in the body can help us appreciate their importance and guide us in managing our overall health.
What are the Types of Fat in the Body?
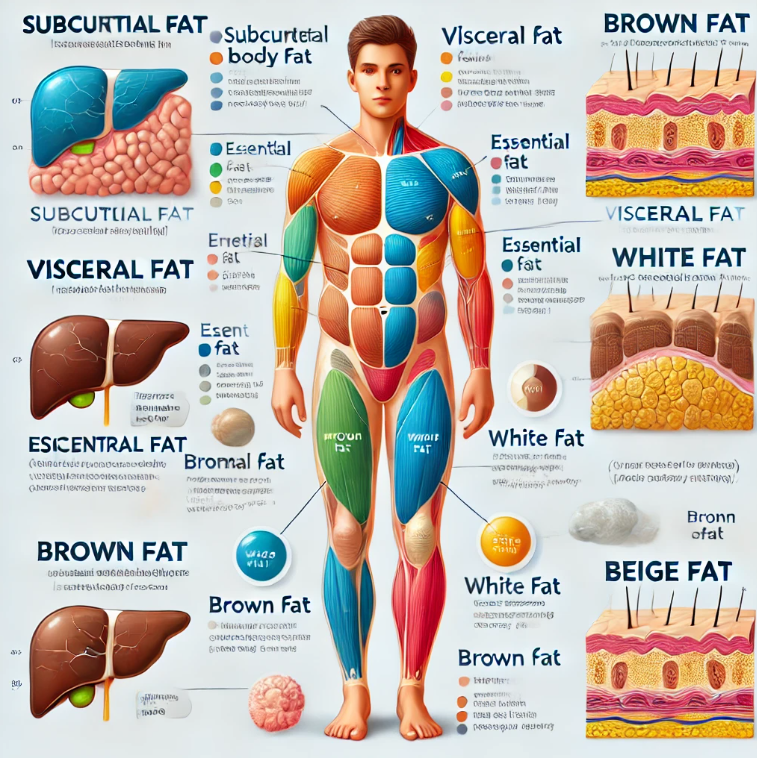
The human body has various types of fats, each serving distinct functions. These include:
1. Subcutaneous Fat
Subcutaneous fat is the most visible type of fat stored just beneath the skin. It serves as insulation to regulate body temperature and provides a cushion to protect muscles and bones.
2. Visceral Fat
This type of fat surrounds the internal organs in the abdominal cavity. While some visceral fat is necessary, an excess can lead to serious health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic disorders.
3. Essential Fat
Essential fat is crucial for survival. It is found in small amounts in organs, bone marrow, and the central nervous system. It helps regulate hormones, supports cell structure, and maintains overall physiological health.
4. Brown Fat
Brown fat is a metabolically active type of fat that helps generate heat by burning calories. It is more prevalent in infants and decreases with age but can still be activated in adults through exposure to cold temperatures.
5. White Fat
White fat stores energy and releases hormones that regulate hunger and metabolism. While necessary in moderate amounts, excessive white fat storage is linked to obesity and related conditions.
6. Beige Fat
Beige fat is a hybrid of white and brown fat, capable of burning energy under certain conditions, such as exposure to cold or exercise.
| Type of Fat | Primary Function | Location | Health Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subcutaneous | Insulation, cushioning | Under the skin | Necessary, but excess can lead to cellulite |
| Visceral | Protects organs, energy | Around internal organs | Excess can cause heart disease or diabetes |
| Essential | Vital for survival | Bone marrow, organs, CNS | Critical for hormonal and structural balance |
| Brown | Heat generation | Upper back, neck | Helps in burning calories |
| White | Energy storage | All over the body | Excess leads to obesity and metabolic issues |
| Beige | Energy burning (conditionally) | Found in white fat regions | Activates in response to cold or exercise |
Where is Most Fat Stored in the Human Body?
Fat storage patterns vary between individuals, influenced by genetics, age, sex, and lifestyle. Typically:
- Males tend to store fat around the abdominal area (visceral fat), which poses a higher health risk.
- Females often store fat in the hips, thighs, and buttocks (subcutaneous fat), a pattern associated with lower health risks.
Understanding these patterns is crucial, as it highlights the difference between the types of body fat in males and the types of body fat in females.
Importance of Fats in Our Body
Fats are essential for the following functions:
- Energy Source: Fat provides 9 calories per gram, making it a dense source of energy.
- Nutrient Absorption: Vitamins A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble, meaning they require fat for absorption.
- Hormonal Balance: Fats regulate hormone production, particularly for reproductive and growth hormones.
- Protection and Insulation: Fat cushions vital organs and maintains body temperature.
Two Types of Fat in the Body: Dietary vs. Stored
Fat can be categorized into dietary fats (fats we consume) and stored fats (fats within the body). Here’s how they differ:
| Aspect | Dietary Fats | Stored Fats |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Found in food | Stored within the body |
| Types | Saturated, unsaturated, trans, and omega-3 | Subcutaneous, visceral, essential, etc. |
| Function | Provides energy, aids absorption | Stores energy, insulates body |
| Example | Butter, olive oil, avocado | Belly fat, thigh fat |
Types of Fats in Food
- Saturated Fat: Found in animal products like butter and cheese. Should be consumed in moderation.
- Unsaturated Fat: Found in nuts, seeds, and fish. Known as “healthy fats.”
- Trans Fat: Artificial fats found in processed foods, which should be avoided.
6 Types of Body Fat
When discussing the types of body fat, it is essential to focus on both their function and impact. These include:
- Subcutaneous Fat: Visible under the skin; contributes to body shape.
- Visceral Fat: Surrounds organs; excess can lead to health risks.
- Essential Fat: Critical for life processes; found in small amounts.
- Brown Fat: Burns calories; contributes to heat generation.
- White Fat: Stores energy; dominant in the body.
- Beige Fat: Burns calories under specific conditions.
How to Manage Fat Levels
- Balanced Diet: Include healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil while minimizing trans fats and excess saturated fats.
- Regular Exercise: Aerobic activities and strength training can reduce white and visceral fat while enhancing brown and beige fat activity.
- Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep can disrupt fat metabolism and increase visceral fat accumulation.
- Stress Management: High stress leads to cortisol release, encouraging visceral fat storage.
FAQs about Types of Fats in the Body
1. What are the types of body fat in females?
Females primarily have subcutaneous fat stored in the hips, thighs, and buttocks, which plays a role in reproductive health.
2. What are the types of fats in food?
There are four main types: saturated, unsaturated, trans fats, and omega-3 fatty acids.
3. Where is most fat stored in the human body?
Most fat is stored as subcutaneous fat beneath the skin and visceral fat around internal organs.
4. What are the two types of fat in the body?
The two broad categories are essential fat (necessary for survival) and stored fat (subcutaneous, visceral, brown, etc.).
5. What are the 6 types of body fat?
The six types include subcutaneous, visceral, essential, white, brown, and beige fat.
6. What is the importance of fats in our body?
Fats provide energy, support hormonal functions, insulate the body, and assist in nutrient absorption.
7. How is fat distributed differently in males and females?
Males store more visceral fat in the abdominal area, while females store subcutaneous fat in the hips and thighs.
8. How can subcutaneous fat be reduced?
A combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can reduce subcutaneous fat.


